Comprehensive single-cell genome analysis at nucleotide resolution using the PTA Analysis Toolbox
Sjors Middelkamp, Freek Manders, Flavia Peci, Markus J. van Roosmalen, Diego Montiel Gonzalez, Eline J.M. Bertrums, Inge van der Werf, Lucca L.M. Derks, Niels M. Groenen, Mark Verheul, Laurianne Trabut, Cayetano Pleguezuelos-Manzano, Arianne M. Brandsma, Evangelia Antoniou, Dirk Reinhardt, Marc Bierings, Mirjam E. Belderbos, Rubén van Boxtel.
Cell Genomics VOLUME 3, ISSUE 9, 100389, SEPTEMBER 13, 2023 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xgen.2023.100389
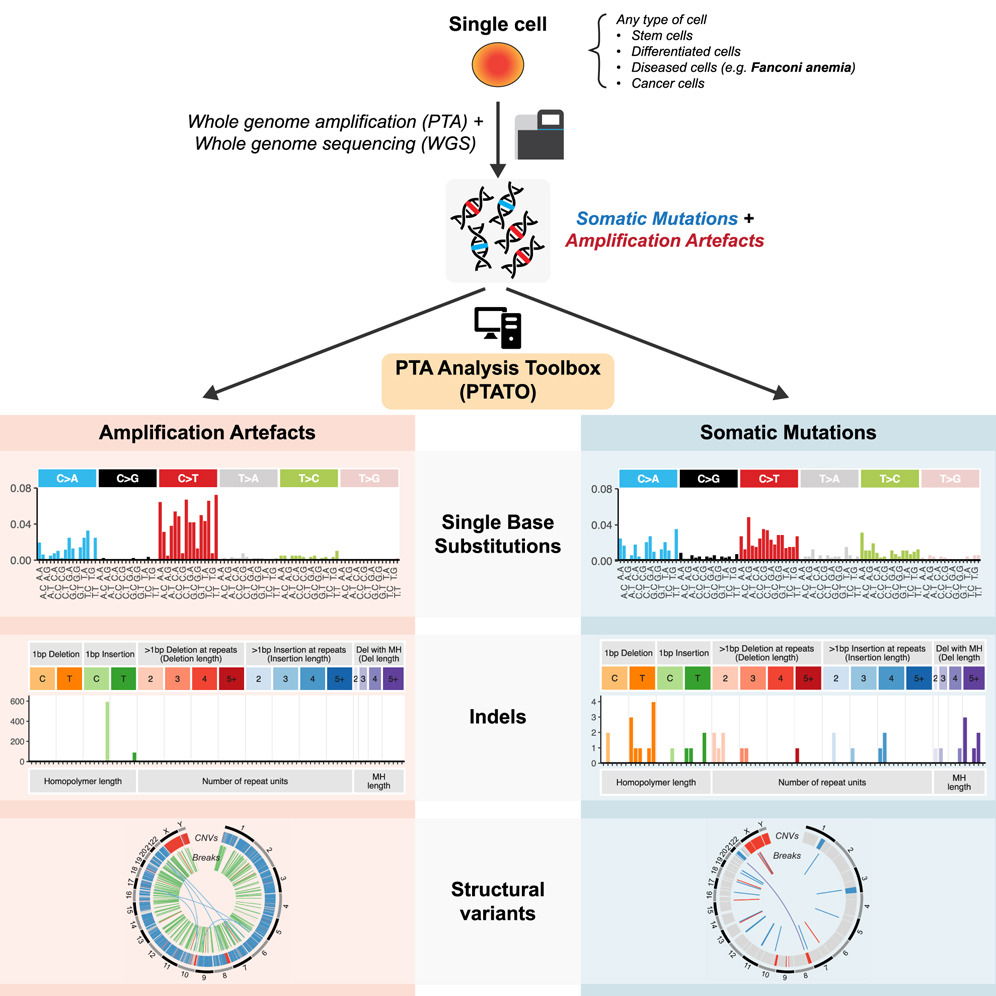
Detection of somatic mutations in single cells has been severely hampered by technical limitations of whole- genome amplification. Novel technologies including primary template-directed amplification (PTA) signifi- cantly improved the accuracy of single-cell whole-genome sequencing (WGS) but still generate hundreds of artifacts per amplification reaction. We developed a comprehensive bioinformatic workflow, called the PTA Analysis Toolbox (PTATO), to accurately detect single base substitutions, insertions-deletions (indels), and structural variants in PTA-based WGS data. PTATO includes a machine learning approach and filtering based on recurrence to distinguish PTA artifacts from true mutations with high sensitivity (up to 90%), out- performing existing bioinformatic approaches. Using PTATO, we demonstrate that hematopoietic stem cells of patients with Fanconi anemia, which cannot be analyzed using regular WGS, have normal somatic single base substitution burdens but increased numbers of deletions. Our results show that PTATO enables study- ing somatic mutagenesis in the genomes of single cells with unprecedented sensitivity and accuracy.


